In modern workspaces, USB power modules and chargers enhance connectivity and collaboration. However, even with new USB regulations from the European Union, which include one universal charger in new devices, businesses may still face challenges. Different USB types, power outputs, and compatibility factors impact charging speeds and efficiency.
This guide will explore USB charging technologies, common compatibility issues that business owners may face, and how to choose the most reliable and efficient USB charger for your workspace.
Click on the relevant link to jump to that section:
What is the difference between USB versions and types?
A USB version refers to the technology standard rather than the shape of the plug or the USB port. The version determines the data transfer speed and charging efficiency.
For example, USB 2.0 has a maximum speed of 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0 can transfer data at 5 Gbps—over ten times faster. Newer versions like USB 3.1 and USB 3.2 improve both speed and power efficiency.
On the other hand, a USB type defines the physical connector and port shape. USB A is the traditional rectangular connector commonly used on computers and wall chargers, while USB C is the newest and most versatile connector.
For more information about USB connector types and how to identify them, read our full guide here.
Understanding USB charging: Types and power outlets
USB, or Universal Serial Bus, refers to transferring data between computers or their components (for example, a mouse or keyboard), as well as various electronic devices. As technology has advanced, there are several types of USB connectors.
Not all USB ports provide the same power, so it’s important to choose the one that best suits your needs regarding the number of USB ports available.
In the table below, compare the different USB types to determine compatibility:
USB Type | Power Output | Device Compatibility | USB Compatibility | Fast Charging? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
USB A 1.1 | 5V/0.1A | Basic peripherals (e.g., keyboards, mice) | USB 1.1, USB 2.0 | ❌ No |
USB A 2.0 | 5V/0.5A | Small accessories, slow phone charging | USB 1.1, USB 2.0, USB 3.0 | ❌ No |
USB A 3.0 | 5V/0.9A | Phones, tablets, external drives | USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1 | ⚠️ Limited |
USB A 3.1 | 5V/1.5A – 20V/5A | Fast charging devices, external SSDs | USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2 | ✅ Yes |
USB B 2.0 | 5V/0.5A | Printers, scanners, older peripherals | USB 1.1, USB 2.0 | ❌ No |
USB B 3.0 | 5V/0.9A | External storage devices, industrial equipment | USB 2.0, USB 3.0 | ⚠️ Limited |
USB C 3.0 | 5V/3A | Phones, tablets, some laptops | USB 3.1, USB 3.2, USB4 | ✅ Yes |
USB C PD | Up to 100W | Laptops, gaming consoles, power banks | USB 3.1, USB 3.2, USB4, Thunderbolt 3 & 4 | ✅ Yes |
USB A vs. USB B vs. USB C: What’s the Difference?
- USB A: This offers standard charging speeds but lacks advanced power delivery capabilities.
- USB B: Typically used for printers, external hard drives, and industrial applications. This type is becoming less common.
- USB C: A newer, more powerful connection type that supports Power Delivery (PD) and faster data transfer.
While USB A is the most common type, it is slowly being phased out by USB C, the latest and most powerful iteration. USB C supports faster data transfer and PD. Unlike USB A and the Type B, USB C is reversible, meaning it can be plugged in either way, making it more convenient.
USB C is also increasingly becoming the standard for charging smartphones, tablets, and laptops, replacing older USB types in new devices. Recent law changes in the European Union require new devices to include the Type C as the USB standard charger. While the UK government has made no official moves to adopt these principles, it is still likely that the USB C will become the most widely used type.
Make sure your workspace is prepared for the future technologies by incorporating different USB charging opportunities.
Our top pick for multi-charging workstation power module
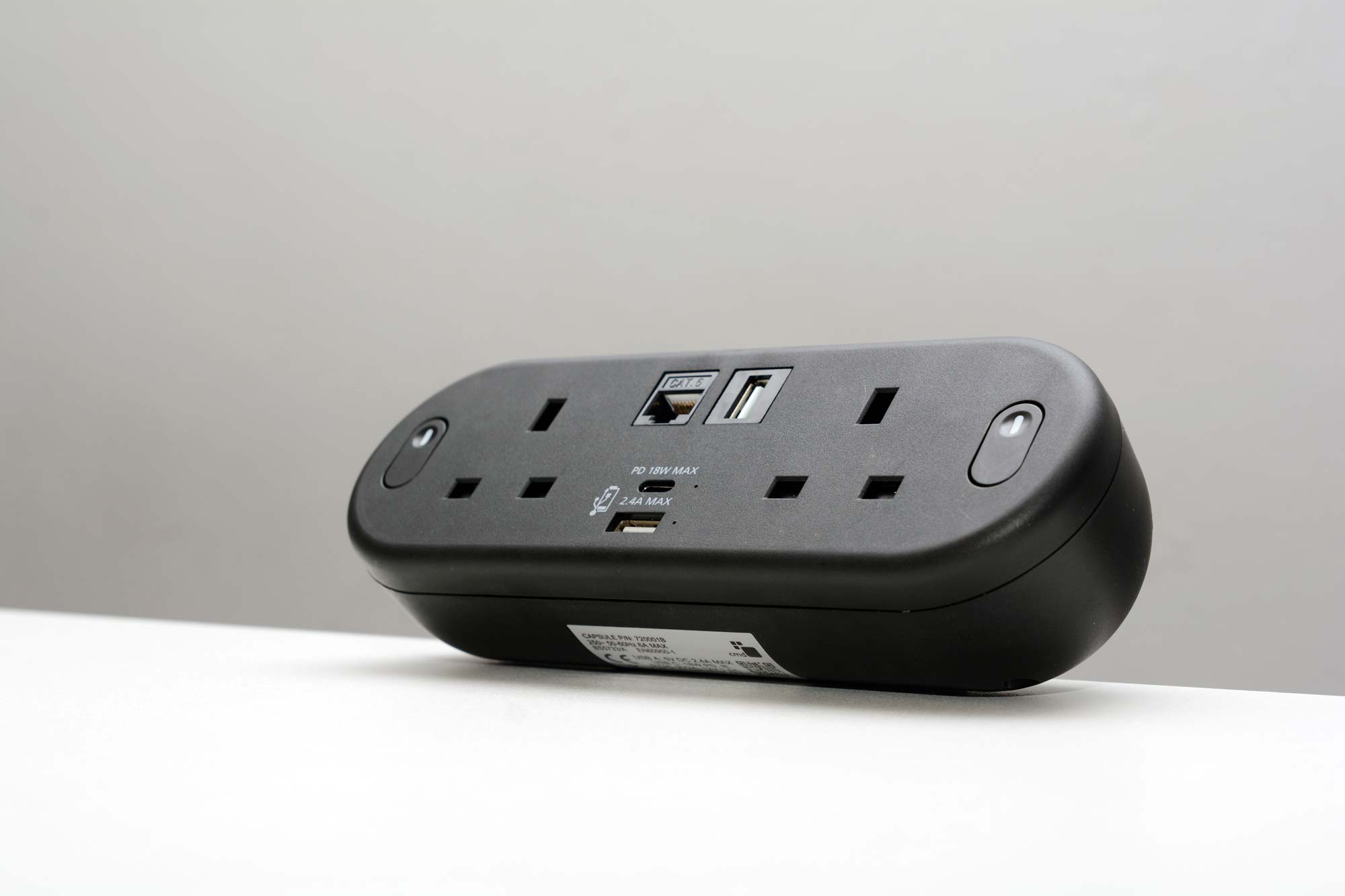

Features:
- Type A and Type C dual port USB fast charger
- 2x UK sockets
- Available in black or white
- Perfect for powering laptops, tablets, and smartphones
Shop the Capsule and Capsule Plus on-desk power module here.
Browse all our workstation power modules here.
Is USB 3.0 backwards compatible?
USB 3.0 is designed to be fully backwards compatible with older USB versions, including USB 2.0 and USB 1.1. This means you can plug a USB 2.0 device into a USB 3.0 port, on a host device, and it will always function properly. However, the usb flash device will only operate at the speed supported by USB 2.0 rather than benefit from the faster speeds of USB 3.0.
Similarly, connecting a USB 3.0 flash drive to a USB 2.0 port will work, but data transfer speeds will be limited to what the USB 2.0 technology can handle. The same principle applies in reverse—plugging an older USB 2.0 device into a USB 3.0 port will not make it transfer data any faster than its original design allows.
One key benefit of USB 3.0 is its ability to provide greater power efficiency while maintaining compatibility with older devices. This makes it a great option for users who must balance modern speed advantages with legacy device connectivity.
Understanding fast charging technologies
Fast charging has become vital for modern devices. Different technologies enhance charging efficiency, with USB C Power Delivery (PD) being one of the most versatile. It dynamically adjusts voltage and current to provide optimal power delivery based on the device’s requirements, making it ideal for smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Qualcomm Quick Charge (QC) increases voltage to charge devices faster while preventing overheating and power surges. Standard USB A ports typically offer 5V/2.4A, but they lack the adaptability and high-speed capabilities of newer USB C alternatives.
Choosing a power module that supports both USB A and USB C ensures backward compatibility while providing access to fast-charging technologies.
Our new workstation on-desk power module:
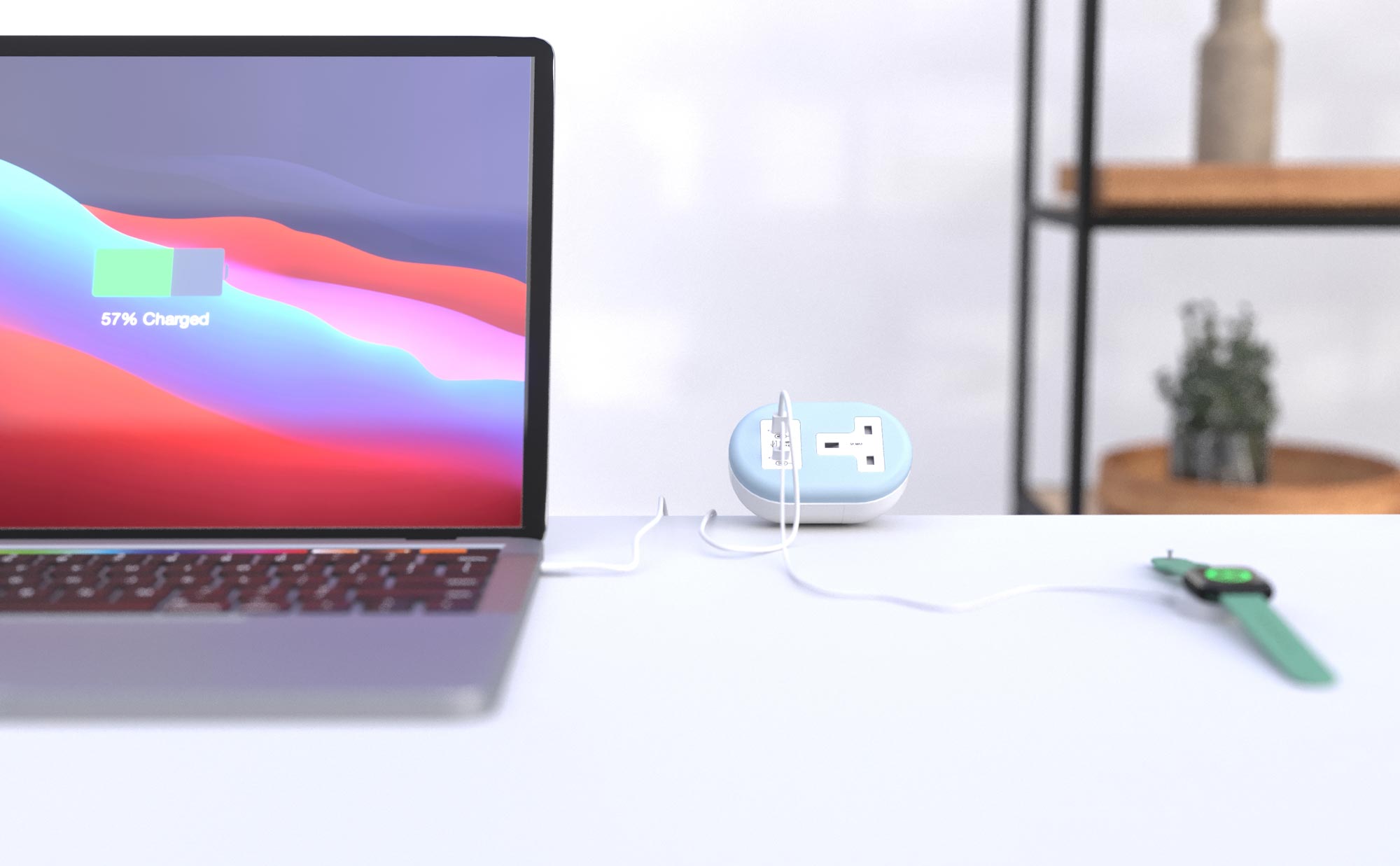

Features:
- Twin USB Type C adaptive fast chargers
- Neat and vibrant
- Available in black and white and other bright colours
- Maximum 65W for charging high-powered laptops and tablets
Shop the Caplet, with twin USB C fast chargers here.
Browse the right USB fast charging power modules for your needs here.
Choosing the right USB charger depends on your devices and usage needs. CMD’s power modules offer a balance of performance, design, and safety, making them ideal for all types of workplaces and collaborative spaces. We provide innovative power modules as well as ergonomic and cable management solutions tailored for modern work environments.
If you have any questions or want a power quotation, contact the CMD team today or call us at 01709 829511.
Frequently asked questions
Why does my device charge slowly even when connected to a fast charger?
Slow charging may be caused by using a low-quality or incompatible cable, power module limitations, or a device that does not support fast charging.
Can I use a USB C charger for my USB A device?
Yes, with an adapter, but charging speed will be limited to the USB A standard.
What is the best USB power module for office use?
CMD offers a range of power modules that cater to different needs and are compatible with a range of high-powered devices. Capsule and Capsule Plus are compact modules with USB A and USB C ports, which are ideal for office desks.
The Porthole Power Module is designed for workstations and offers power sockets alongside USB charging. The Harmony Power Module provides a stylish all-in-one solution with advanced USB C PD compatibility.
Do CMD USB power modules support fast charging?
Select models include USB C PD and Qualcomm Quick Charge for rapid charging.







 Instagram
Instagram